Algeciras
Location: Port of Algeciras Bay in Algeciras.


Climate: The city experiences a Mediterranean climate, characterised by warm, dry summers (up to 30°C) and mild, rainy winters (below 15ºC). Summer and autumn can bring occasional thunderstorms, sometimes accompanied by heavy rainfall and strong winds
Context: Local authorities are driving an integrated port-city action (‘Lago Maritimo’ project) aimed at regenerating Algeciras Bay for developing a new urban area that combines economic, social, and environmental progress. The project also includes the construction of infrastructure for improving the sustainability of urban water cycle.
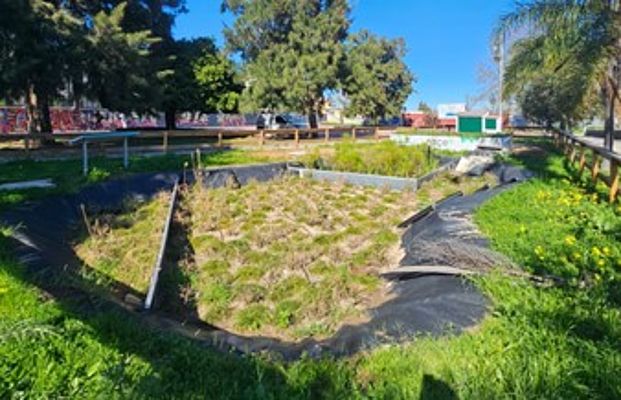
Typology: Multi-stage constructed wetland for grey water and storm water treatment.
Description:
Urban Real Lab Algeciras consists of one shallow basin, divided in two filtering areas, both covered with drought and flood-tolerant plants. Grey water filtre (15 m2) acts as a Horizontal Flow Constructed Wetland(HFCW), where grey water coming from washbasins of an educational institution is treated. Flooding the treatment wetland horizontally favours the anaerobic elimination of nutrients and pollutants. Grey water reaching the bottom of the basin then horizontally flows towards Storm water filtre (70 m2), which acts as a Vertical Flow Constructed Wetland(VFCW). Flooding the treatment wetland vertically favours the aerobic removal of pollutants and nutrient through filtration, adsorption, microbial degradation, etc. Regenerated grey water and storm water is mutually collected and repurposed for irrigation of ornamental gardens.
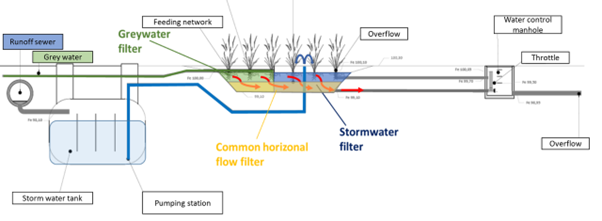
Main innovation:
- Layers of the treatment wetland constructed with absorbent materials.
- Simultaneous treatmentof grey water and storm waterunder real conditions.
- Saturated bottom for water storage (grey water treated + stormwater) to compensate the water loss by evapotranspiration and to avoid the plants irrigation in dry periods.
Synergies:
- CETIM assisted in finding suitable absorbent material to avoid clogging issues.
- INRAE assisted in designing the hybrid wetland output and the saturated layer at the bottom of the constructed wetland.
NICE Urban Real Labs are Nature-based Solutions (NbS) designed and implemented in locations with challenging geographical, environmental and socioeconomic characteristics. Their purpose is to increase the availability of solutions that contribute with water circularity in urban areas. NICE Urban Real Labs cover a wide range of climate zones, including a) Tropical and Subtropical (Pereira and Turin), b) Mediterranean (Algeciras, Benalmadena, Cairo), c) Oceanic (Aarhus), d) Continental (Talavera and Madrid), e) Baltic (Gdansk) and f) transitional between temperate and moderately Continental and Mediterranean (Lyon).

This project has received funding from the European Union's Horizon 2020 research and innovation programme under grant agreement No.101003765.
